World Economic Forum
Why Trade Wars Can't Solve the Problems Brought by Globalization

Source:The White House
We asked policy experts and business leaders: how can countries really reap the economic and social benefits of global value chains (GVCs), while avoiding inequality and environmental damage?
Views
Why Trade Wars Can't Solve the Problems Brought by Globalization
By Aditi Verghese, Sean Dohertyweb only
The Trump Administration’s announcement in February of new steel and aluminium tariffs on national security grounds, including on imports from allies like the EU, have set the stage for escalating trade tensions. The EU recently imposed retaliatory tariffs on products ranging from bourbon whiskey to motorcycles. The US President hit back with a tweet threatening a 20% import tariff on autos and auto parts, telling manufacturers: “Build them here!”
A number of US-based firms have voiced concerns over supply chain disruptions from trade wars. Harley Davidson stated that it would be shifting production aimed at the EU market outside the US to avoid the additional tariff burden, exemplifying the unintended consequences of this approach.
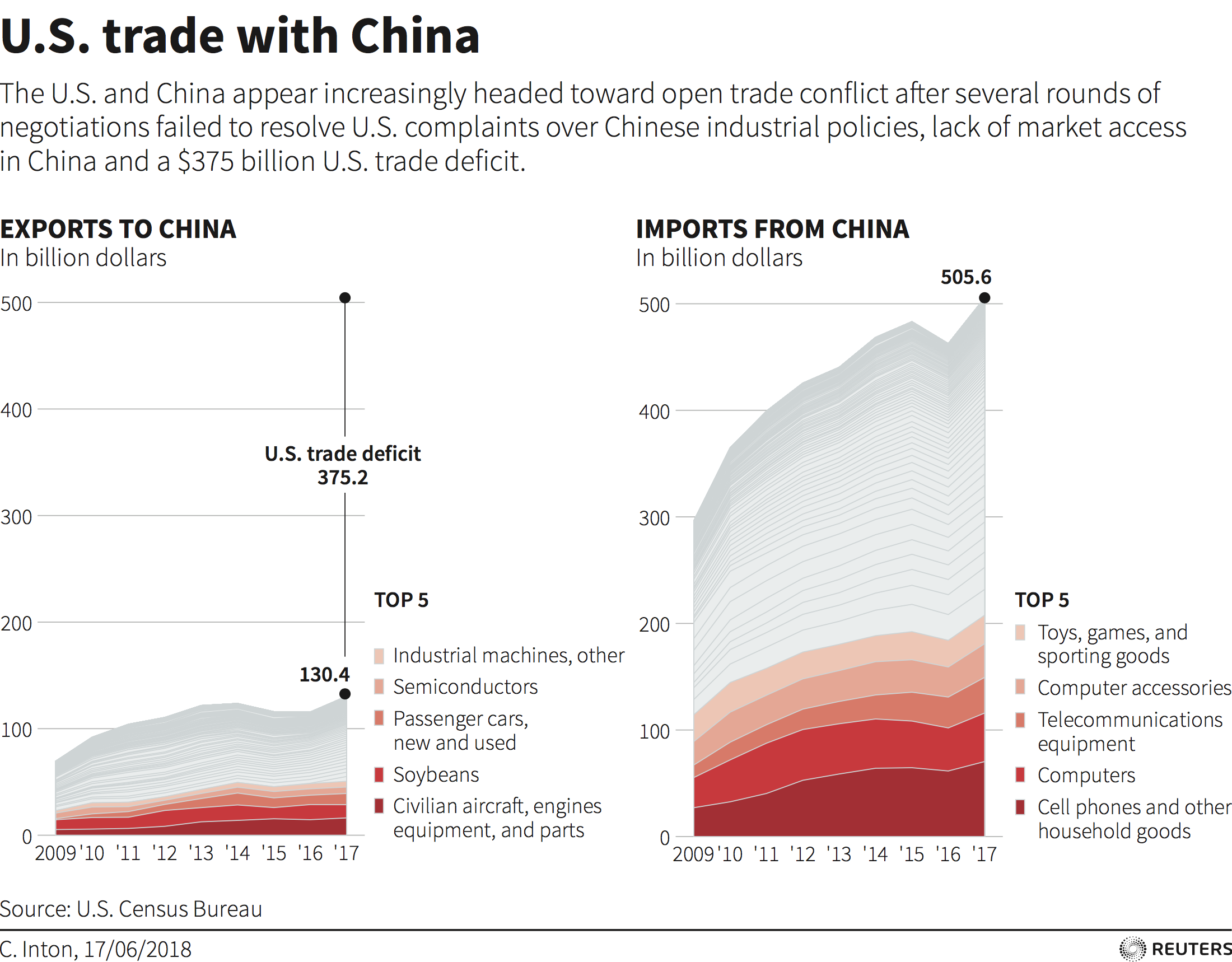
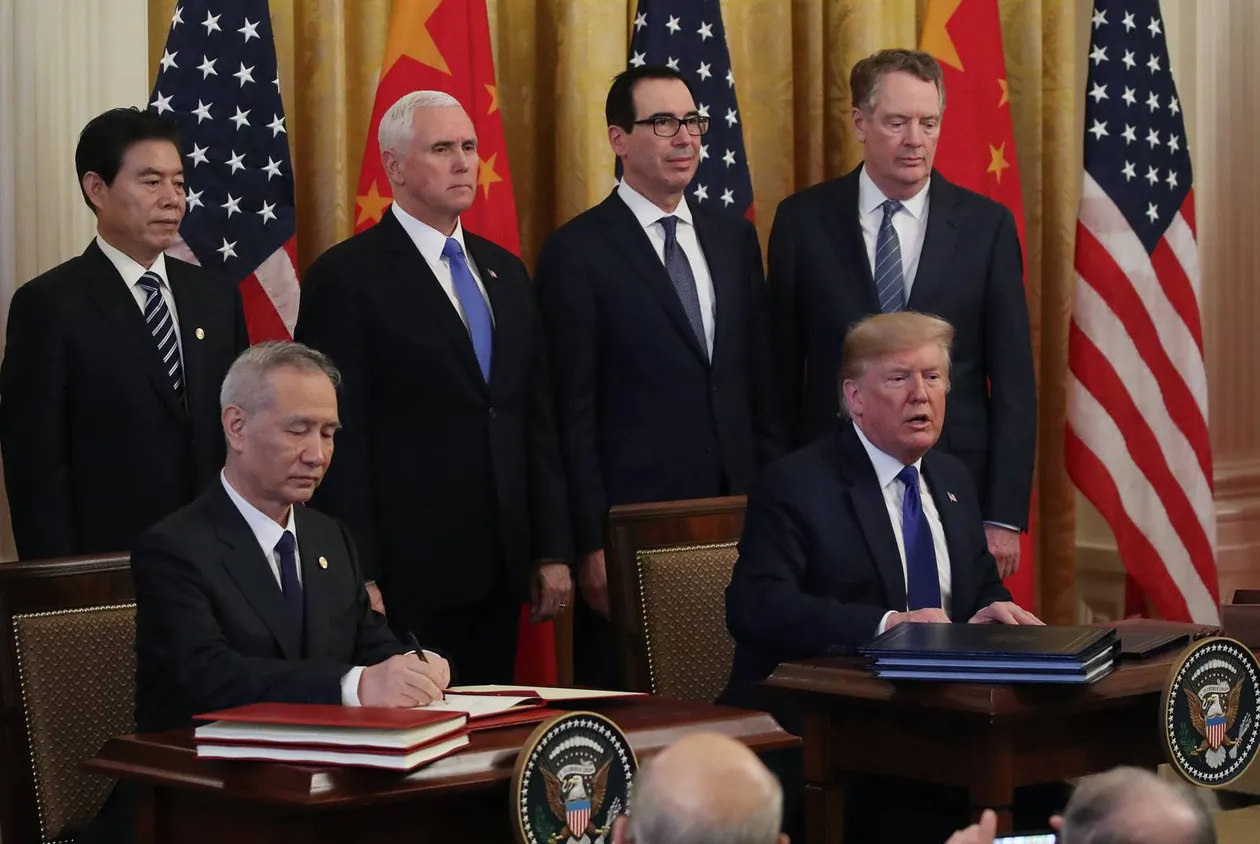
Earlier this month, the US announced a 25% duty on around $50 billion worth of Chinese imports on the grounds that they utilize intellectual property obtained from US firms through forced technology transfers or theft. China’s Made in China 2025 plan was named and scrutinised in the report. UNCTAD estimates that, like China, more than 100 countries have formal industrial policy strategies, many of which involve joining and benefitting from global value chains (GVCs). Tariff wars undermine growth models that rely on the benefits and efficiencies of globalization.
We asked policy experts and business leaders: how can countries really reap the economic and social benefits of GVCs, while avoiding inequality and environmental damage?
Don’t neglect services: Much of the recent talk of bilateral trade deficits has overlooked the importance of services to the global and national economies. Factors affecting services competitiveness have become important for economic growth and development more generally. Investment in human capital, digital infrastructure (including reliable mobile broadband), efficient and flexible domestic regulation and connectedness with international markets (including open cross-border flow of data, visa facilitation and mutual recognition agreements) are key. The services sector has strong inclusiveness dimensions: it is more SME-intensive than the goods sector is and has more women workers, owners and managers.
Co-operate on competition policy: Various anti-competitive activities by firms impede the efficient operation of value chains. Today, there are over 100 jurisdictions administering competition law. In the absence of global rules on competition, each jurisdiction applies its own system. Firms can find themselves facing conflicting decisions from different authorities with respect to the same merger or other activity. This leads to the most interventionist ruling of a major economy being enforced. In the case of digital products, questions of jurisdiction and enforcement are all the more challenging. Greater cooperation between agencies would improve clarity and reduce gaps in enforcement.
Prioritise tax certainty over incentives: In an attempt to attract GVC-linked foreign direct investment (FDI), many countries engage in harmful tax competition to woo multinational enterprises (MNEs). However, for the most part, FDI tends to be more sensitive to tax certainty than to tax incentives. Enhanced consistency in tax rules, interpretation and enforcement across economies and better cooperation between authorities help foster certainty. That being said, tax credits for education and training could help build a workforce suited for high-demand tasks through public-private partnerships. These and other programmes would need to be designed and monitored carefully to avoid tax evasion or aggressive tax planning by MNEs.
Incentivise sustainability: MNEs play a key role in coordinating activities and actors along the value chain. They set private standards that suppliers and affiliates have to meet. An increasing number (over 550) of these standards are sustainability-related. As these can be difficult for small producers to navigate and meet, coherent standards and simplified procedures are needed. Many big, consumer-facing brands are seeing greater demand for sustainably-sourced products from their customers. Others are finding ways to raise capital by tapping into investor appetite for sustainable business operations.
Implement doing-business reforms: Since MNEs play such an important role in GVCs, creating an enabling environment that attracts and sustains FDI is crucial. This involves reforms that cut red tape and corruption, improve infrastructure, provide quality education to the workforce to enable them to work in modern production chains and ensure that companies operating in the country have access to foreign exchange so that they can pay suppliers and repatriate profits.
So far, the tariff war has been just that: a tariff war, limited to the use of import duties on goods. Soon, though, the US is expected to release details of how it plans to restrict Chinese investment in US companies where it deems it a threat to national security. Meanwhile, the Chinese government could make things difficult for US companies operating in China – by imposing regulatory burdens or encouraging consumer boycotts. It could choose to block mergers, such as the one proposed between the US firm Qualcomm and Dutch firm NPX. The EU could consider retaliating against US banking and insurance companies and taxing digital services, hurting US tech companies.
Short-sighted, protectionist measures ignore and erode the opportunities that GVCs provide for driving inclusive and sustainable growth and do nothing to optimize outcomes.
Edited by Shawn Chou
Additional Reading
♦ A Turning Point for Globalization
♦ Terry Gou’s U.S. Gambit: The Eagle Has Taken Off
♦ Formosa Plastics’ Shift to America
Original content can be found at the website of World Economic Forum.
♦ Trade wars won’t fix globalization. Here’s why
This article is reproduced under the permission of World Economic Forum (WEF) and terms of Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 Unported License (“CCPL”). It presents the opinion or perspective of the original author / organization, which does not represent the standpoint of CommonWealth magazine.