The path to resilience: Circular supply chain outlook for Taiwan and Europe

Source:Jang-Hwa Leu
Taiwan has built a close partnership with European countries. As the EU has actively promoted the circular economy policy and related regulations, it is essential to enhance practical cooperation between Taiwanese industries and European brands.
Views
The path to resilience: Circular supply chain outlook for Taiwan and Europe
By Jang-Hwa Leuweb only
Introduction
Taiwan has built a close partnership with European countries. In response to the transformation of the circular economy, the industrial cooperation conference jointly held by the Industrial Development Bureau (IDB) and European countries in recent years has started the discussion of circular economy.
IDB continues promoting the "Circular Economy Promotion Plan" within the “Five plus Two Industrial Innovation Plan,” and deepens the circular cooperation with European countries to help the domestic companies improve the efficiency of energy and resource use, promote industrial symbiosis and transformation, and create a win-win solution together with the global supply chain.
Building the circular supply chain has become an international trend
To improve the efficiency of energy resource use and to reduce the impact of production on the environment, international brands have been gradually implementing the concept of circular economy into supply chains, transforming the original linear supply chains into circular supply chains. A circular supply chain refers to the continuous recycling of products and resources throughout the economy. Compared with a linear supply chain, a circular supply chain puts more emphasis on the communication and cooperation within an industry, enhancing information sharing and building a transparent environment to create high-quality products and services.
Sustainable products have become increasingly popular. To keep up with changes in consumer behaviour, global brands are transforming into circular business models. Many brands have set quantifiable circular economy goals, including that of their supply chains. In addition, the national governments, depending on their current situation of domestic industrial development, constantly enact new circular economy laws on different aspects including production, consumption and recycling. In the foreseeable future, Taiwanese industries can potentially cooperate with European brands to create more green business opportunities.
Circular economy policy of Taiwan
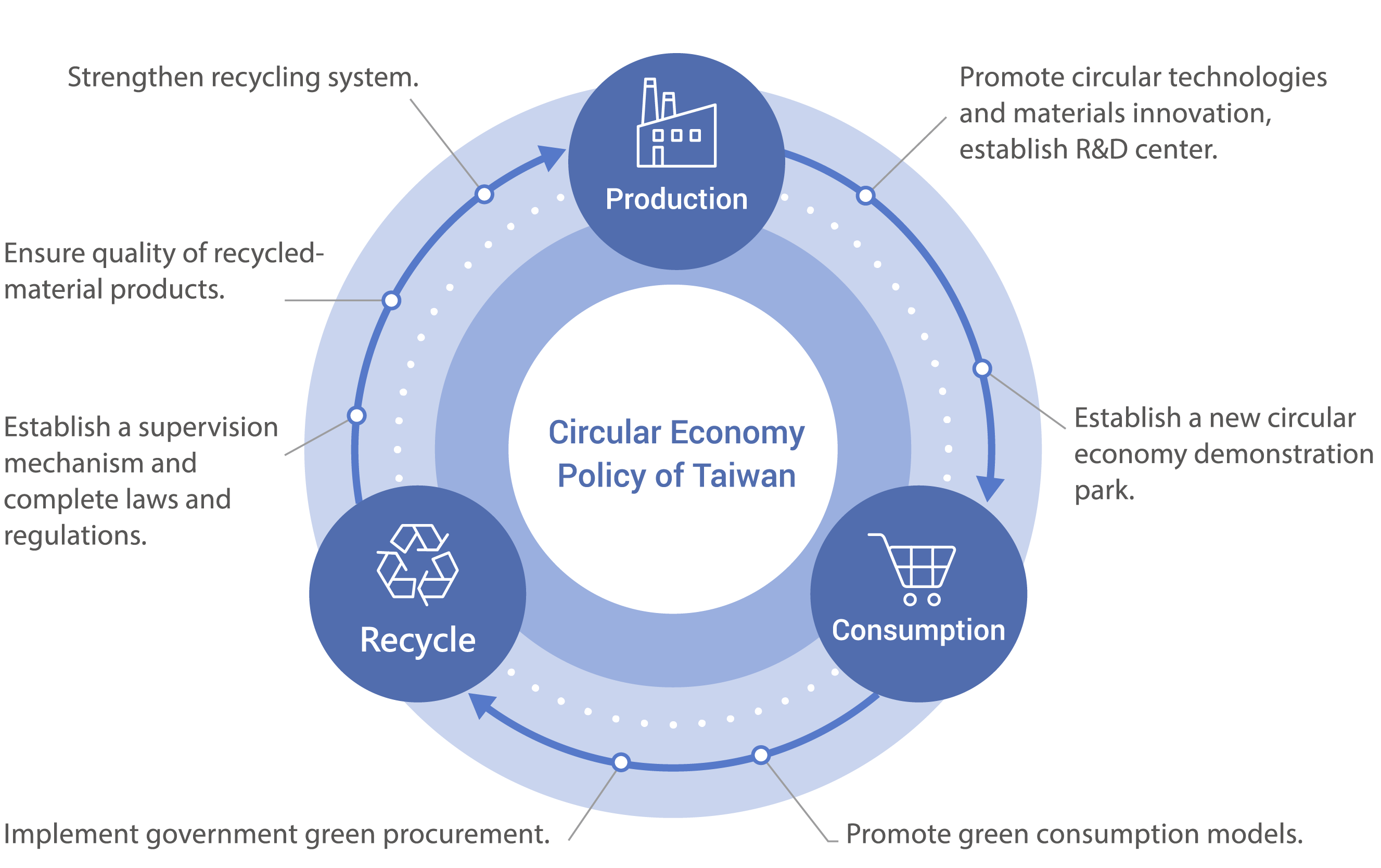 The information was consolidated by Industrial Development Bureau (IDB). Figure: Taiwan's Circular Economy Policy
The information was consolidated by Industrial Development Bureau (IDB). Figure: Taiwan's Circular Economy Policy
The Executive Yuan approved the "Circular Economy Promotion Plan" in December 2018 by three core aspects - "green production," "green consumption," and "recycling and reuse," with the aims of " Making Industries Circular " and " Making Circularity an Industry." We plan to improve the efficiency of energy and resource integration, to promote industrial symbiosis and transformation, and to strengthen international competitiveness by investing in R&D, technology, land, talents and capital for the circular economy.
To implement “green production,” we promote integration of cross-regional resources and industrial symbiosis and construct circular economy demonstration parks by introducing professors from the top domestic universities to cooperate with the industry. We invest in the research and development of new recycled and high-value materials, to carry out recycling and low-carbon production in the recycling park, and to realize the commercialization of circular products. To promote “green consumption,” we encourage the public infrastructures to use secondary material for the purpose of reducing the negative impact of production on the environment. For “waste recycling and reuse,” we focus on the cooperation among the manufacturing, consuming, and recycling sectors to assist the industries in implementing a circular economy and linking the global supply chain.
Circular economy policy of the EU
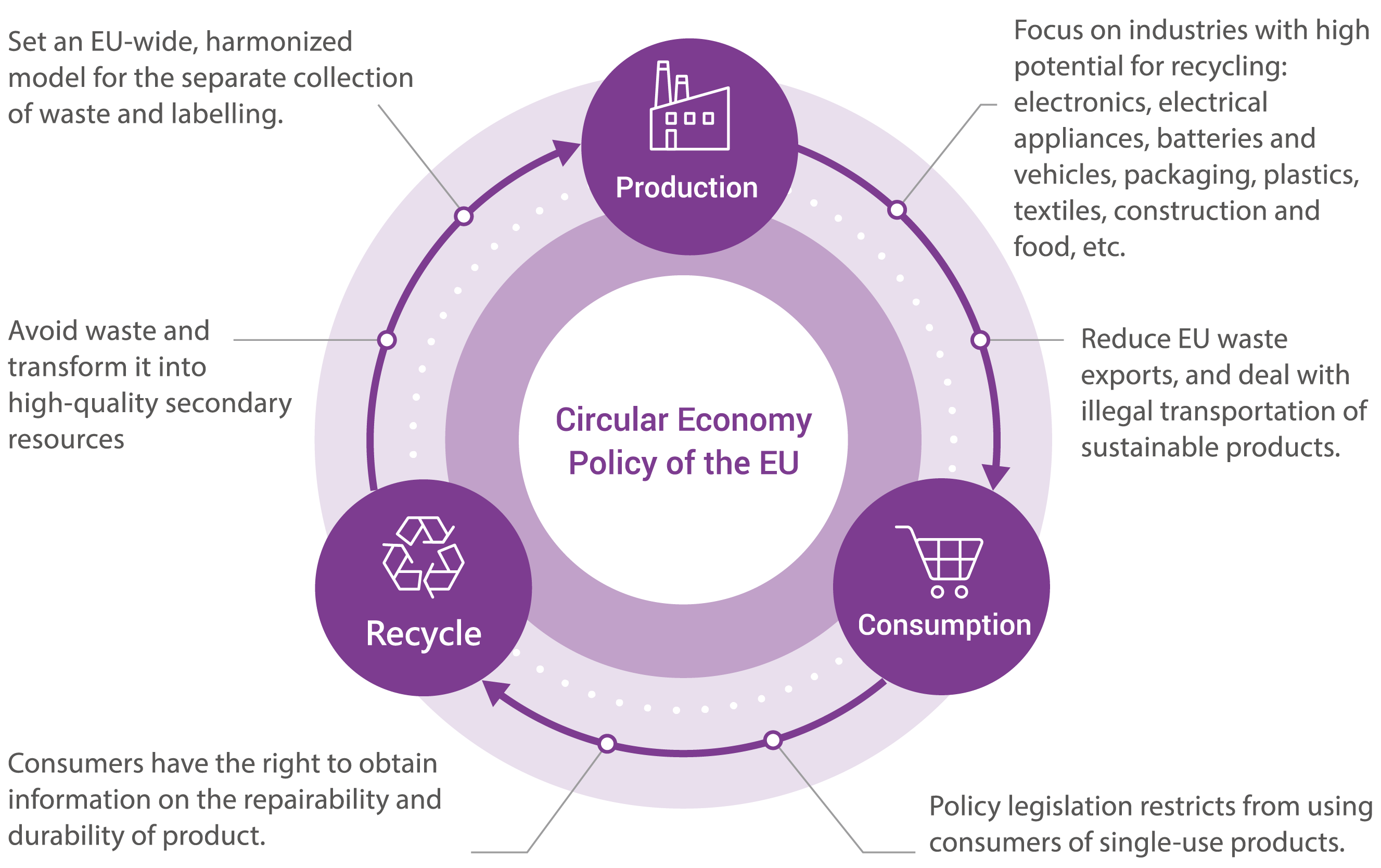 The information was consolidated by Industrial Development Bureau (IDB). Figure: EU's Circular Economy Policy
The information was consolidated by Industrial Development Bureau (IDB). Figure: EU's Circular Economy Policy
The European Union is one of the most active regions in the promotion of global circular economy policies and regulations. Following the revised "Circular Economy Action Plan" (CEAP) in 2020, along with the "European Green New Deal," the EU has gradually developed a series of regulations and policies. Under the goals of "Carbon Neutrality" and "Zero Waste," it hopes to accelerate the research and development of recycling technology and the transformation of the global supply chain.
The New Circular Economy Action Plan of the European Commission strongly emphasizes the development of sustainable products. It also focuses on resource-intensive industries, such as plastics, textiles, electronics, batteries and construction, and is supplemented by the regulation of recycled industrial waste. More importantly, it issues relevant laws and regulations, such as the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) and Single-Use Plastic Directive (SUPD). It implements strategic alliances between industries in the value chain. For example, SUPD stipulates PET bottles and all bottles must contain 25% of recycled materials by 2025 and 30% of recycled materials by 2030, respectively.
Conclusion
 2018 International Conference on the Circular Economy organized by Industrial Development Bureau (IDB) and co-organized by European Chamber of Commerce – Low Carbon Initiative (ECCT LCI).
2018 International Conference on the Circular Economy organized by Industrial Development Bureau (IDB) and co-organized by European Chamber of Commerce – Low Carbon Initiative (ECCT LCI).
As the EU has actively promoted the circular economy policy and related regulations, many European brands must select green supply chain vendors that comply with circular procurement regulations when seeking the international partners. On the other hand, Taiwan has efficient recycling systems and outstanding green soft technologies. It is essential to enhance practical cooperation between Taiwanese industries and European brands.
Since 2018, IDB has been working with ECCT LCI to organize a circular international conference, workshops, and matching events on the circular economy. In the previous events, we had speakers and guests from governmental organizations (e.g., the British Office Taipei, etc.), international organisations (e.g., RE100, the Carbon Trust, International Synergies Limited, and Bianna Recycling, etc.), global brands (e.g., Apple, Dell, and Scania, etc.) and the representatives from domestic recycling companies, etc.
Moreover, IDB has established the Brand-Supply Chain Matching Mechanism to accelerate the cooperation between brands and domestic suppliers. The mechanism matches circular supplies and demands, and speeds up brands’ searching process for suitable supply chains. To find out more details about the circular supply chain policy and business consultation services, please follow the upcoming report, “The Path to Resilience: Circular Supply Chain Outlook for Taiwan and Europe.”
About the author:

Mr. Jang-Hwa Leu
Director General, Industrial Development Bureau, Ministry of Economic Affairs
The mission of the Industrial Development Bureau (IDB) of the Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA) is to promote industrial development. With the SDGs goals, IDB provides consultation services to the domestic industries to reduce GHG emissions and to improve energy and resource efficiency to enhance industrial competitiveness.
Have you read?
♦ How ESG investors jolted Foxconn into taking climate action
♦ Far Eastern New Century: Partner in sustainability for top global brands
♦ TSMC’s bold net zero pledge: Cutting a Taipei’s worth of emissions
Uploaded by Penny Chiang






